An Introduction to Security Camera Systems.
by Amanda Hughes

360° Security Cameras Installed in Warehouse
Researching security camera systems for your home or business can be overwhelming. With many different types of cameras on the market, determining the ideal camera for your situation can be tricky. This is why it is important to have your security camera systems installed by a professional integrator who will be able to accurately determine the best types of cameras for your needs. Here, we will describe the most commonly used cameras for professional installations as well as some camera types you may never have heard of.
The Basics

Dome Cameras
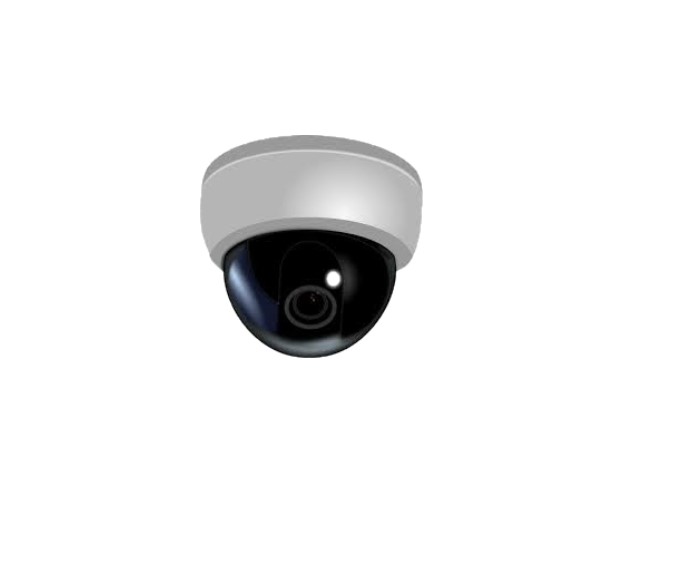

The most common type of camera used for both indoor and outdoor designs are dome cameras. They shaped like a dome and made to withstand the weather inside and outside. The IR LEDs incorporated into these cameras allow them to function in low- or no-light situations. Dome cameras offer the benefit of flexible installation. They often are vandal-resistant. Because of their covert design, it is nearly impossible to tell where the camera’s lens is pointing. These cameras are the most vandal-resistant and have the lowest profile thanks to their design.
Bullet Cameras

The term “bullet camera” refers to the device’s distinctive cylindrical design, which resembles a lipstick tube or a bullet shell. Bullet cameras, one of the most popular kind of security cameras, serve as an obvious deterrent. In fact, research show that having security cameras makes your house less appealing as a target. Similar to dome cameras , they can be mounted both indoors and out. The range and installation of bullet cameras are their key advantages. Due to its long range, bullet cameras are perfect for monitoring expansive areas like parking lots and backyards. Bullet cameras are easy to install. Bigger lenses can be fitted to its body due to it’s unique shape. The bullet camera’s tip has a slight lip that helps shield against glare and rain, making it ideal for outdoor use.
Turret Cameras
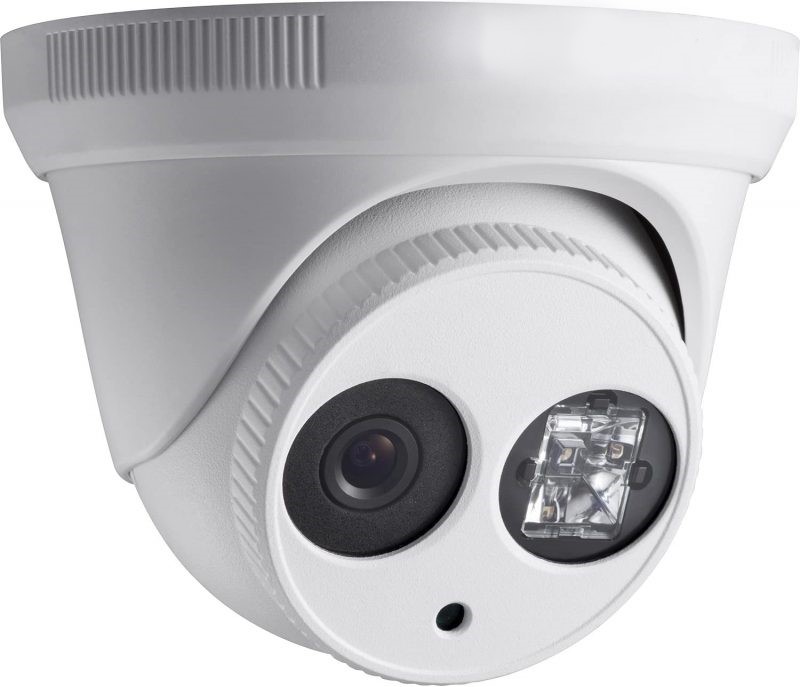

Turret cameras have a ball-and-socket structure. Also referred to as eyeball or flat-faced dome cameras. Once the base is attached, it can be readily rotated in its “socket.” The turret camera uses infrared (IR) and EXIR for it’s night vision capabilities. Thanks to the EXIR technology available on turret cameras, the illumination pattern is uniformly distributed and rectangular. Compared to infrared cameras, EXIR turret security cameras can provide a higher luminance efficiency and a greater night vision range. When placed outside, such as in your doorway, backyard, front driveway, soffit, or eave, turret cameras are increasingly more popular than dome and bullet security cameras. They lack the bullet style’s ability to attract spider webs and the dome type’s reflecting problems.
PTZ Cameras

A pan, tilt, and zoom (PTZ) camera is a robotic video camera that can pan horizontally, tilt vertically and diagonally, and zoom in on a subject to improve the image quality without digital pixellation. A joystick controller, an IR remote, and software are just a few of the controls available for PTZ cameras. IR remote controls often only provide a small number of fundamental capabilities for operating the camera and accessing presets. The IR remote controls are simple to use. The camera requires close installation to the operator in order for the IR controls to function. Operators often use software to manipulate far away cameras.
Varifocal Cameras
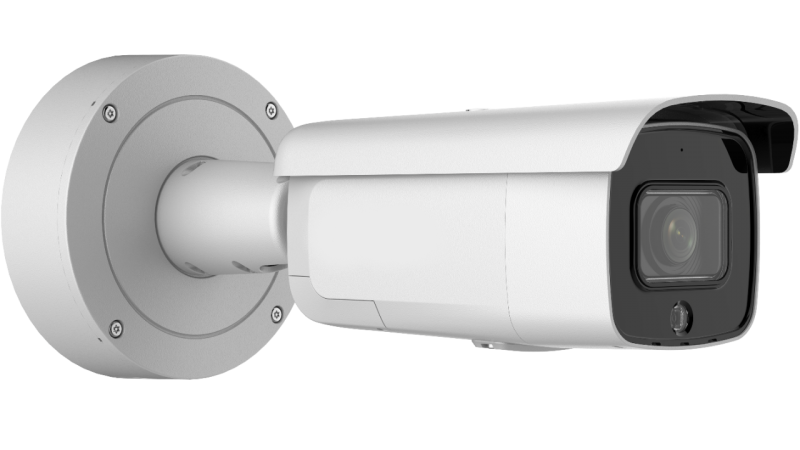
Varifocal cameras enable you to adjust the lens on the camera until you have the perfect field of view. This capability functions only during the installation, unlike PTZ models. The field of view can’t change after the initial installation. Varifocal cameras have a ‘zoom’ range, which most commonly goes from from 2.8 to 12mm. A range of 5 to 60mm is typical for long-range surveillance such as license plate recognition cameras.
The main advantage of a varifocal camera is the positioning flexibility it provides. They enable you to move the lens between its top and bottom view angle limits.
Unique Cameras
Some of the more unique cameras available to consumers typically serve a specific purpose. License plate cameras for residential communities , explosion proof cameras on industrial oil rigs or military bases, thermal cameras to detect trespassers on private property…these all use advanced technology to specialize in a specific type of detection.
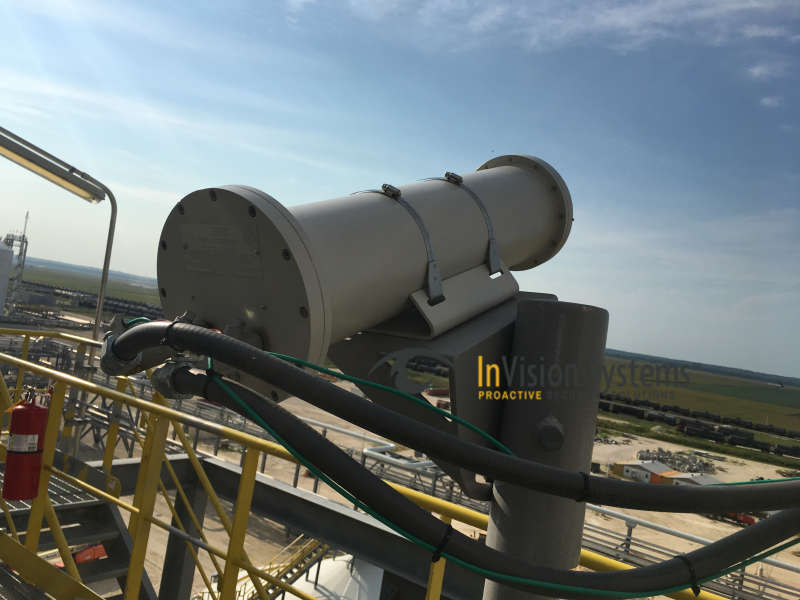

The Explosion Proof camera is designed does not cause explosions. Many people assume that they are designed to withstand an explosion. Made with enclosures that prevent sparks from igniting the gas or dust in the environment and certified by the ATEX and UL standards. The enclosures can either contain any internal explosion within the camera using inert gases or the housing can be strong enough to prevent an internal explosion from escaping outwards.
License Plate Cameras (LPRS) are designed to recognize and record license plates, even from a far distance. These cameras use advanced infrared technologies to extract numbers and letters, reading the plate. Contrary to popular belief license plates are very difficult to pick up on traditional security camera systems (whether the vehicles are idle or moving), especially at night when traditional cameras are unable to process the reflecting light bouncing off of the plate. In some cases, databases of license plates can be kept to recognize authorized plates and accurately report on unauthorized plates.
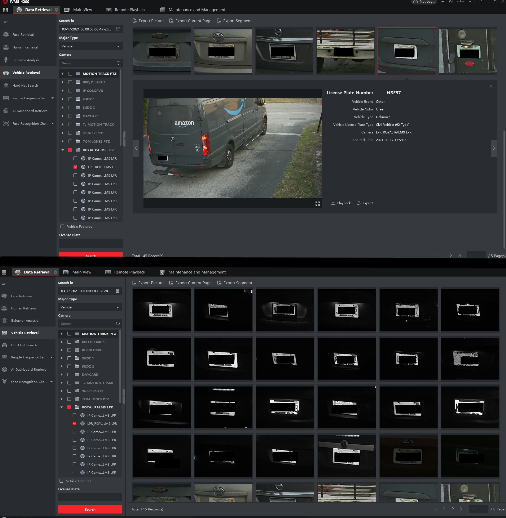

Thermal imaging cameras use infrared energy to create thermal images. Thermal cameras can detect humans from up to 9 miles away with thermal imagery. Even at night, intruders can be easily detected, despite dark clothing or camouflage.
What are IP cameras vs TVI Cameras?
TVI Cameras
TVI cameras offer high definition picture quality and are a cost-effective security choice. TVI cameras operate by recording images and transferring the signal to a DVR (Digital Video Recorder), which is normally linked directly to the cameras, through a coax cable. Additionally, the coax connection does not provide power to the camera while sending video data to the DVR. TVI cameras will require separate power sources. The DVR compresses the video file, transforms it from an analog to a digital signal, and then saves it on a hard disk. Monitors connected to the DVR allow you to view the cameras. Alternatively, the DVR can broadcast the video over the internet via an internal network by connecting to a router and modem.
IP Cameras
IP (Internet Protocol) cameras are rapidly replacing analog cameras as the industry standard. IP security cameras are digital cameras that transmit or receive data over the internet. In order to meet your unique security requirements, IP cameras are available with a variety of features and technologies. A Network Video Recorder (NVR) and a single Power-over-Ethernet (PoE) connection are used to link wired IP security cameras. IP security camera systems can effectively and efficiently manage massive volumes of information because they transmit their signal across a network. So, without sacrificing quality or service, it is feasible to broadcast video, audio, camera status data, metadata, configuration, and motion commands.
Indoor cameras or Outdoor Cameras?
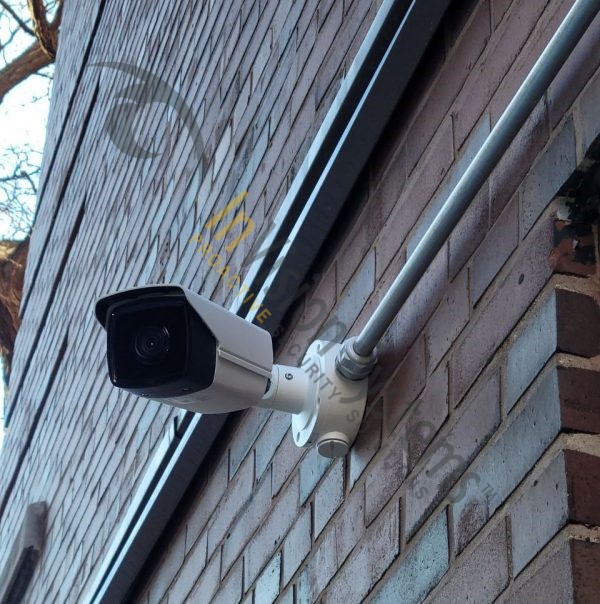

With the many options of types of cameras available, you may be wondering if it makes any difference where you install your cameras. The short answer is yes. The cameras available today are typically rated for outdoor use. Your security professional will make sure the cameras installed are practical whether you are installing the cameras inside a facility or in the parking lot.
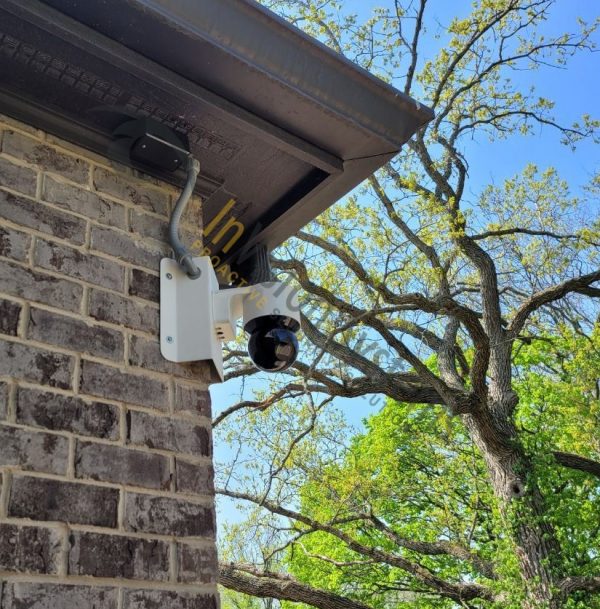

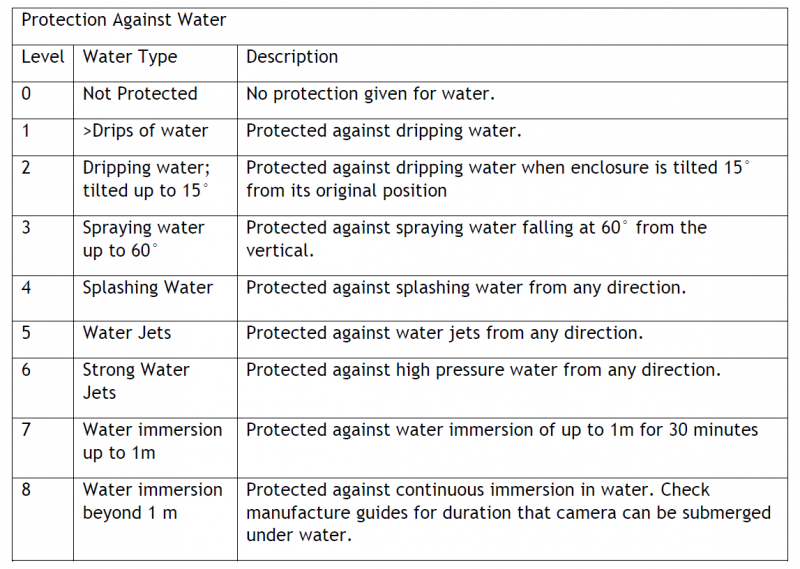
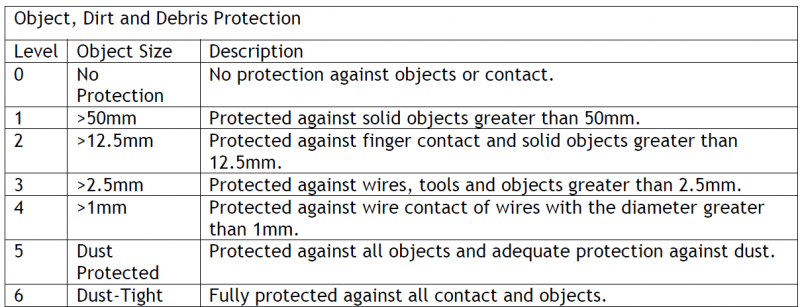
Cameras are rated using the IP rating system or Ingress Protection Rating System. This system is designed to tell you how resistant the equipment is to dust and liquids. This was developed to provide consumers with information about how weatherproof a camera enclosure is. These ratings are given as a two digit code, such as IP55 or IP66. The first digit represents the level of protection against dust and the second digit to liquid. The higher the number, the stronger the level of protection. For indoor use, for example, you can use a camera with an IP rating of <44. This camera will withstand typical dirt and debris and even a small amount of rain (a camera with this rating is not intended for water submersion). Whereas a camera with an IP rating of 69, will be able to withstand all dust and debris and can survive long immersion periods under water. Most applications will utilize a camera with an IP rating of 67, which is weatherproof.
Whether your application calls for indoor cameras to monitor employees and patrons or outdoor cameras to monitor your entrances and parking lots, there is a camera solution for you.

NVR vs DVR

NVR and DVRs are both used for video recording. DVR stands for Digital Video Recorder and NVR stands for Network Video Recorder. The main distinction between an NVR and DVR is how they process video information. DVRs process the video information at the recorder and NVRs encode and process the video information at the camera. Then it is streamed to the NVR which is used for storage and remote viewing. As DVRs and NVRs handle the video data differently, they require different kinds of cameras. Most NVRs are used with IP cameras whereas DVRs are used with TVI cameras. These devices store your cameras information, configuration settings and, most significantly, your recorded video data. They are equipped with high memory hard drives to store hundreds of hours of video data. These devices also allow you to manage your system. Video recordings are stored locally on the system and are available to be viewed or saved at your discretion. Typically these devices include back up battery systems which ensure that video continues to record in the event of network or power outages.
Today’s network storage devices have features like high-capacity storage that can be expanded with growth; RAID protection against hard drive failures; remote access; small to large camera count support; and cloud backup options. Some are even equipped with software to provide some analytic features that send notifications or alerts to end users as configured.
Security Camera Systems Data: Cloud Storage vs Local Video Management
Local Storage
Local management can be done two ways. First, you can access your camera system directly from your Network Video Recorder or Digital Video Recorder (NVR, DVR). This is where all of your video data is being stored locally. Directly from this device you can view your system live, view past recordings or change configurations.
Another way to manage the system locally is to have a dedicated PC to run the cameras specific video management software. This is a great option if you need discretion with your security camera systems or do not have a monitor connected directly to your DVR or NVR. This local software, usually offered by the manufacturer, will give you all of the option of viewing your system directly from the DVR or NVR, but may have some added or additional features available. With local video management software , you are capable of accessing your security cameras remotely through a browser or mobile application. Your NVR or DVR can be configured during installation to allow remote viewing so long as you have an internet connection. This gives administrators of the system flexibility to manage users, review or export video clips or simply peek into your camera systems live view from anywhere with an internet connection.
Cloud Storage

As the name suggests, cloud storage is a way to store surveillance footage online. Cloud camera solutions are increasingly gaining popularity as an alternative to on-premise recorders like NVRs and DVRs With cloud storage, video content is kept on distant servers and made practically accessible from any location with an internet connection. Cloud surveillance solutions, unlike local security camera systems, do not need technical configurations (such as opening ports and firewalls) to enable remote accessibility.
Remote access to video data is available for security personnel, business owners, and other authorized users via any smart device or browser. Data may be seen and controlled across several places because the video data is saved in the cloud. Users of cloud storage have the opportunity to increase their data storage capacity to fulfill the needs of expanding organizations. End users can easily adapt to their needs for video retention because of this scalability.
When compared to local storage, using cloud storage for video data is far less expensive, but both options come with benefits and drawbacks. For instance, there is an initial cost for the hardware with on-premise recorders, such as an NVR or DVR. There are fees connected with storing your video data, typically in the form of a monthly subscription, even though the majority of cloud systems do not require the same head end equipment. Ultimately, the decision lies in what you hope to get out of your system. Small residences may do well with local storage, requiring only a small amount of data storage. While a large manufacturing facility may require multiple servers running on the cloud with higher data limitations.
Security Camera Systems : What’s next?
Analytics and New Technologies

Video analytics has one main goal, which is to automatically recognize certain events in videos. A person who moves or enters a facility suspiciously, motor vehicles entering a parking garage, unauthorized entry onto lots; these are just a few examples of what analytics can detect. This then will trigger an alert or notification sent directly to the administrator of the system, allowing them to react in real time.
Many manufacturers continue to develop software applications with smarter and more refined analytic capabilities.

Analytics for security camera systems have come a long way. Once only available for military applications, analytics are quickly becoming standard features. As newer technologies advance, the need for smarter analytics grows. So what are smart analytics? Let’s dig in to some of the basic analytic features typically available.
Intrusion detection/Line crossing: Line crossing allows you to add a line or lines to a specific camera that should not be crossed. If the line that has been set is crossed, the NVR can begin recording and send an alert or even sound an alarm. Line crossing is ideal for fence lines, property monitoring and parking areas that should not be entered.
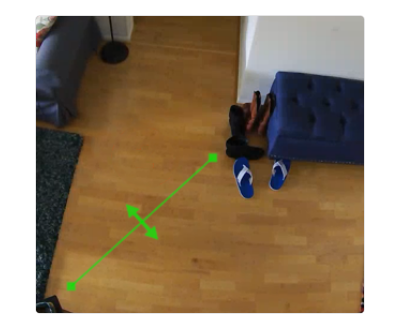

Object detection/ground zone: Movement is detected within an entire scene or in a designated area and is defined by setting what is called a ‘Ground Zone’. An object appearing in a designated area and remaining there for longer than a preset time can be detected and reported. There is also the capability to ‘count’ objects or people within the same zone. These instances can then trigger notifications. Objects can also be set based on size or type to further specify necessary detection.
More advanced analytics include Facial Recognition, body temperature detection and heat mapping.

Facial recognition identifies and confirms someones identity using their face. This is a form of biometric security. This technology can be used to identify individuals in real time or in photos and videos. Facial recognition technology uses 2D images to match public photos or photos in a database. Facial recognition software reads the geometry of a face, using key points such as how far apart your eyes are or how your lips are contoured to identify your distinctive facial landmarks. This works much the same as fingerprint as the software creates a unique analysis of each face, turns it into data using a numerical code and that code is your ‘facial fingerprint’. You may see this technology used at border crossings, on your cellular device or even your local law enforcement agency.
Covid-19 has changed the way our world works. Over 2 million people have been diagnosed with this incredibly contagious virus since 2020. To help curtail the spread, businesses are looking for non-invasive ways to detect individuals who may be infected. Body temperature detection is very effective as they can identify a high temperature, even when the individual may not realize they are sick. Body temperature detection employs the same technology as thermal imaging cameras. These use infrared technology to map the heat signatures in the environment. The higher the heat signature, the more red or orange your image will show. These cameras can accurately detect a temperature to within 0.5°F.

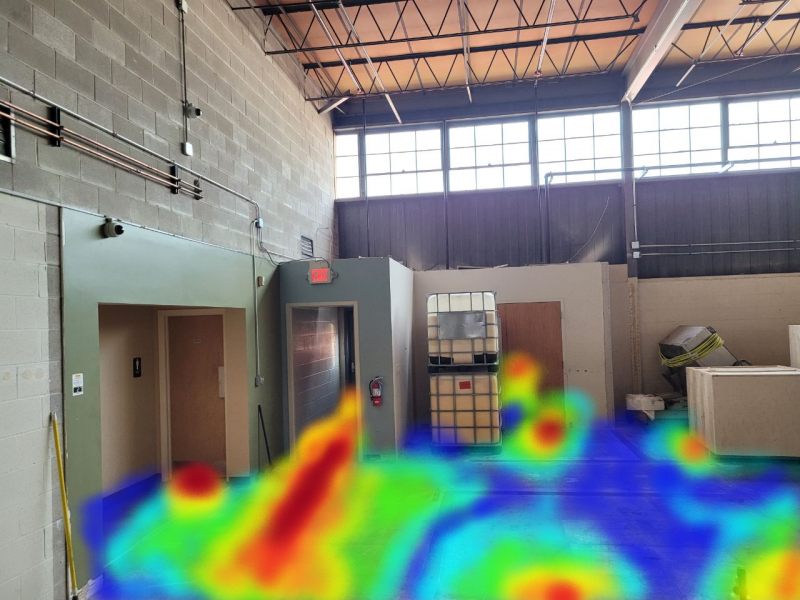
Heat mapping is an analytic tool that can help organizations visualize behavior within the facility. Heat maps can show what aisles customers frequent in a retail setting or depict a visual chart of areas that may be congested with foot traffic. Heat mapping can also be useful in a warehouse facility where monitoring the heat signature in a particular building or area is paramount to regulatory safety standards.
Understanding the different types of security camera systems available enables you to make an informed choice when considering the security of your home or business.
